The subroutine GSWN establishes a window, or rectangular subspace, of world
coordinates to be plotted.
If you desire
log scaling or
mirror-imaging of axes, use the
SET
subroutine.
-------------------------------------------------
Argument | Type | Mode | Dimension
-------------------------------------------------
CALL GSWN (TRNUM, | Integer | Input |
XMIN, | Real | Input |
XMAX, | Real | Input |
YMIN, | Real | Input |
YMAX) | Real | Input |
-------------------------------------------------
- TRNUM
- A normalization transformation number. The number of available
transformations is implementation specific. In the case of NCAR GKS, two
normalization transformations are provided:
- 0
- Refers to the identity transformation in which both the window and
viewport have the range of 0. to 1. in both dimensions.
This is the default normalization transformation for GKS.
This transformation is standrdized within GKS and it cannot
be changed. It will always be the identity transformation and
attempts to redefine it will produce an error.
- 1
- A normalization transformation in which the window is
defined by XMIN to XMAX and YMIN to YMAX.
- XMIN
- The left horizontal coordinate of the window.
-
- XMIN < XMAX
- XMAX
- The right horizontal coordinate of the window.
- YMIN
- The bottom vertical coordinate of the window.
-
- YMIN < YMAX
- YMAX
- The top vertical coordinate of the window.
- Defaults:
- The default normalization transformation is transformation 0,
the identity transformation.
- Errors:
- 7,
20,
25,
33,
36,
51,
53
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
C Synopsis
#include <ncarg/gks.h>
void gset_win(
Gint tran_num, /* transformation number */
const Glimit *win_limits /* window limits */
);
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The subroutine GSVP establishes a rectangular subspace of normalized device
coordinates.
If you desire
log scaling or morror-imaging of axes, use the
SET
subroutine.
-------------------------------------------------
Argument | Type | Mode | Dimension
-------------------------------------------------
CALL GSVP (TRNUM, | Integer | Input |
XMIN, | Real | Input |
XMAX, | Real | Input |
YMIN, | Real | Input |
YMAX) | Real | Input |
-------------------------------------------------
- TRNUM
- A normalization transformation number. The number of
available transformations is implementation specific. In the case of
NCAR GKS, two normalization transformations are provided:
-
- 0
-
- Refers to the identity transformation in which both the window
and viewport have the range of 0. to 1. in both dimensions.
This is the default normalization transformation for GKS.
This transformation is standrdized within GKS and it cannot
be changed. It will always be the identity transformation and
attempts to redefine it will produce an error.
-
- 1
-
- A normalization transformation in which the viewport is
defined by XMIN to XMAX and YMIN to YMAX.
- XMIN
- The left horizontal coordinate of the viewport.
- XMAX
- The right horizontal coordinate of the viewport.
0.<= XMIN < XMAX <= 1.
- YMIN
- The bottom vertical coordinate of the viewport.
- YMAX
- The top vertical coordinate of the viewport.
0. <= YMIN < YMAX<= 1.
- Defaults:
- The default normalization transformation is transformation 0,
the identity transformation.
- Errors:
- 7,
20,
25,
33,
36,
51,
54
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
C Synopsis
#include <ncarg/gks.h>
void gset_vp(
Gint tran_num, /* transformation number */
const Glimit *vp_limits /* viewport limits */
);
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To select a predefined transformation from
world coordinates to
normalized device coordinates, use the following call:
---------------------------------------------------
Argument | Type | Mode | Dimension
---------------------------------------------------
CALL GSELNT (TRNUM) | Integer | Input |
---------------------------------------------------
- TRNUM
- A normalization transformation number. The number of
available transformations is implementation specific. In the case of
NCAR GKS, two normalization transformations are provided:
-
- 0
-
- Selects the identity transformation in which both the window
and viewport have the range of 0. to 1. in both dimensions.
-
- 1
-
- Selects a normalization transformation in which the window
and viewport have been defined by calls to GSWN and GSVP,
or the SPPS utility
SET.
- Default:
- If GSELNT is never called, the default normalization transformation
is 0 (the identity transformation).
- Errors:
- 8,
50
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
C Synopsis
#include <ncarg/gks.h>
void gsel_norm_tran(
Gint tran_num /* transformation number */
);
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
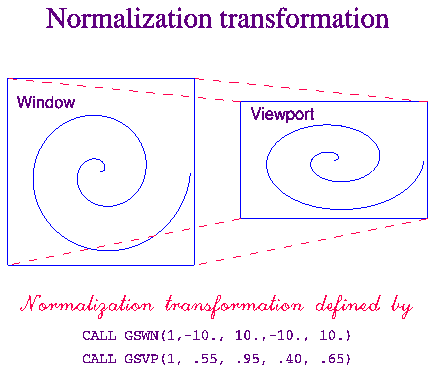
Figure 4
- A GKS normalization transformation
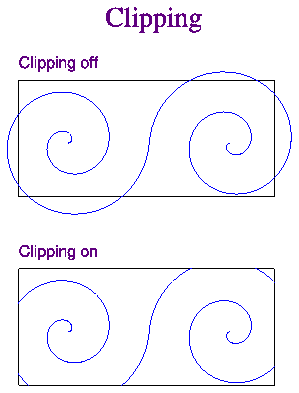
The clipping indicator
controls whether or not data are displayed outside the
boundaries of your defined
viewport. If the clipping indicator is off, and
you make GKS output calls to plot
world coordinate data outside your
defined world coordinate
window (and your viewport is smaller than the full
plotting surface), those data will appear with your plot. If the clipping
indicator is on, the data will be clipped to fit your window. To change
the clipping indicator, issue the call:
---------------------------------------------------
Argument | Type | Mode | Dimension
---------------------------------------------------
CALL GSCLIP (ICLIP) | Integer | Input |
---------------------------------------------------
- ICLIP
- An indicator specifying whether clipping is on or off:
-
- 0 - Clipping is off. Data outside of the window will be plotted.
-
- 1 - Clipping is on. Data outside of the window will not be plotted.
- Default:
- By default, clipping is on.
- Errors:
- 8,
2000
--------------------------------------------------------------------
C Synopsis
#include <ncarg/gks.h>
void gset_clip_ind(
Gclip_ind clip_ind /* clipping indicator */
);
--------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------
Argument | Type | Mode | Dimension
----------------------------------------------------
CALL GQMNTN (ERRIND, | Integer | Output |
MAXTRN) | Integer | Output |
----------------------------------------------------
- ERRIND
- Error flag. Gives an integer error number from the
Errors list in
Appendix D,
or a 0 if no error occurred.
- MAXTRN
- Gives the maximum number of normalization transformations
available in the GKS package. In the case of NCAR GKS, MAXTRN = 2.
- Errors:
- 8
----------------------------------------------------------------------
C Synopsis
#include <ncarg/gks.h>
void ginq_max_norm_tran_num(
Gint *err_ind, /* error indicator */
Gint *max_num /* max trn. number */
);
----------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------
Argument | Type | Mode | Dimension
----------------------------------------------------
CALL GQCNTN (ERRIND, | Integer | Output |
TRNUM | Integer | Output |
----------------------------------------------------
- ERRIND
- Error flag. Gives an integer error number from the Errors
list in
Appendix D,
or a 0 if no error occurred.
- TRNUM
- Gives the current normalization transformation number.
In the case of NCAR GKS the CTNR options are:
- 0
- The window and viewport range from 0. to 1. in both the
horizontal and vertical dimensions.
- 1
- The window and viewport have been set by a previous call to
SET
or by previous calls to GSWN and GSVP.
- Errors:
- 8
----------------------------------------------------------------------
C Synopsis
#include <ncarg/gks.h>
void ginq_cur_norm_tran_num(
Gint *err_ind, /* error indicator */
Gint *tran_num /* transformation number */
);
----------------------------------------------------------------------
If you have defined your normalization transformation by using
GSWN and GSVP, then GQNT should be used to retrieve window and
viewport limits. If you have used
SET
to establish your normalization transformation, then you should use
GETSET
to retrieve window and viewport limits. GETSET will also return the
mirror imaging and
log scaling information.
--------------------------------------------------
Argument | Type | Mode | Dimension
--------------------------------------------------
CALL GQNT (NTNR, | Integer | Input |
ERRIND, | Integer | Output |
WINDOW, | Real | Output | 4
VIEWPT) | Real | Output | 4
--------------------------------------------------
- NTNR
- Gives the number of the normalization transformation
- ERRIND
- Error flag. Gives an integer error number from the Errors
list in
Appendix D,
or a 0 if no error occurred.
- WINDOW
- The horizontal and vertical window limits in the order WXMIN, WXMAX,
WYMIN, WYMAX. Window limits are in world coordinates.
- VIEWP
- The horizontal and vertical viewport limits in the order VXMIN, VXMAX,
VYMIN, VYMAX. Viewport limits are in normalized device coordinates.
- Errors:
- 8,
50
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
C Synopsis
#include <ncarg/gks.h>
void ginq_norm_tran(
Gint num, /* transformation number */
Gint *err_ind, /* error indicator */
Gtran *norm_tran /* normalization transformation */
);
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------
Argument | Type | Mode | Dimension
----------------------------------------------------
CALL GQCLIP (ERRIND, | Integer | Output |
ICLIP | Integer | Output |
CLRECT) | Real | Output | 4
----------------------------------------------------
- ERRIND
- Error flag. Gives an integer error number from the Errors list in
Appendix D,
or a 0 if no error occurred.
- ICLIP
- Gives the value of clipping indicator as set by GSCLIP.
- 0 -- clipping is off, no clipping.
- 1 -- clipping is on. Data outside of the window will not be plotted.
- CLRECT
- The four coordinates of the clipping rectangle in the
order XMIN, XMAX, YMIN, YMAX. The clipping rectangle is in normalized
device coordinates.
- Errors:
- 8,
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
C Synopsis
#include <ncarg/gks.h>
void ginq_clip(
Gint *err_ind, /* error indicator */
Gclip *clip_ind_rect /* clipping indicator and rectangle */
);
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Links:
GKS Index,
GKS Home

