Faraday's Law
From QED
Maxwell's equations describe the propagation of light ( electromagnetic waves) through a medium. Maxwell's equations in Gaussian units are:
Faraday's law:
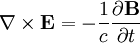
Ampere's law:
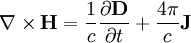
Poisson equation:
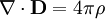
Absence of magnetic monopoles:
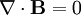
The Lorentz force:
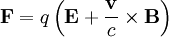
Other relations:

In a plasma, 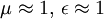
This page was recovered in October 2009 from the Plasmagicians page on Maxwell's_equations dated 21:04, 10 April 2007.