2003 I 4
From QED
The ion cyclotron frequency is:
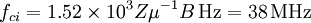
The electron cyclotron frequency is:
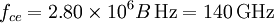
The plasma frequency is:
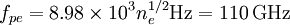
The ion plasma frequency is:
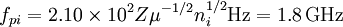
The source frequency is:
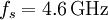
So:
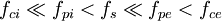
The cold, electrostatic dispersion relation is:
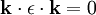
Or:
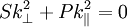
Since 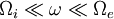 :
:
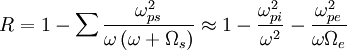
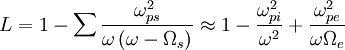
So:
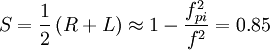
And:
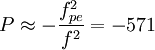
So:
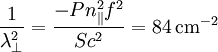
So 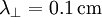 .
.
We can calculate 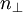 :
:
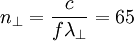
Since 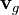 is approximately parallel. Therefore the power will flow in the toroidal direction.
is approximately parallel. Therefore the power will flow in the toroidal direction.
This page was recovered in October 2009 from the Plasmagicians page on Generals_2003_I_4 dated 02:24, 7 May 2007.