Solov'ev's Solution
From QED
Solov'ev's Solution is the simplest two dimensional analytical solution to the inhomogeneous Grad–Shafranov equation.
As a reminder, the so called source functions of the Grad-Shafranov equation are defined by F = rBT, with r the radial distance from the axis of symmetry, and p, the pressure. ψ represents the flux function.
In Solov'ev's solution the source functions are defined simply as
p(ψ) = − p'ψ + p0
and
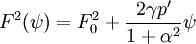
Where a prime denotes derivation by ψ, and γ and α are constants. When γ is set to 0, there is no toroidal field, yielding a Field Reversed Configuration.
Solving the Grad-Shafranov equation, we get
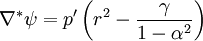
Yielding the solution
![\psi = \frac{p'}{2 (1 - \alpha^2)} \left[{(r^2 - \gamma) Z^2 + \frac{\alpha^2}{4} (r^2 - r^2_0)^2 }\right]](../../images/math/a/e/c/aec150e3479cd3b7e6da54b1279f0298.png)
Solov'ev's solution is simple and exact, but there is afforded little flexibility in the current distribution, making it difficult to fit to many systems of interest.
== Reference ==
S. Solov’ev, Sov. Phys. JETP 26, 400 (1968); Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 53, 626 (1967).
This page was recovered in October 2009 from the Plasmagicians page on Solov'ev's_Solution dated 21:00, 6 July 2007.