Binomial Theorem
From QED
In the discrete case, the Binomial Theorem is
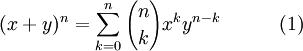 </dd>
</dd>
where 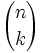 is the binomial coefficient .
is the binomial coefficient .
which may be proven with induction.
In the case continuous case, where r is any complex number and | x / y | < 1, or r is a positive integer,
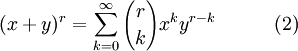 </dd>
</dd>
Where :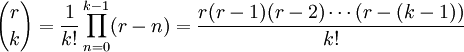
Which may be proven by taking the power series of the left hand expression.
As useful form of this holds for the reciprocal power
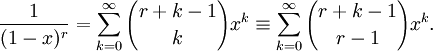 </dd>
</dd>
Which the geometric series is a special case of when r = 1.
This page was recovered in October 2009 from the Plasmagicians page on Binomial_Theorem dated 06:05, 16 October 2006.